Research cluster: ChemBiofilm / Subproject |
| Subproject 6: Chemical analysis of biofilm inhibition and chemical synthesis |
| Project time: 01.02.10-31.10.13 |
| Project leader: |
| Prof. Dr. Stephanie Grond, Eberhard-Karls-Universität Tübingen |
| The aim of the project 'new anti-biofilm strategies from the metagenomes' as part of the GenoMik-Transfer-program (financed by Federal Ministry of Education and Research) is the identification of new biofilm inhibitors to prevent the formation of biofilms. In order to use the potential capacity of so-far non-cultivated organisms, metagenome strategies are utilized. The investigations of bioactive anti-quorum-sensing samples are performed by the interdisciplinary joint project with methods of molecular biology, biochemistry, medicine and organic chemistry. |
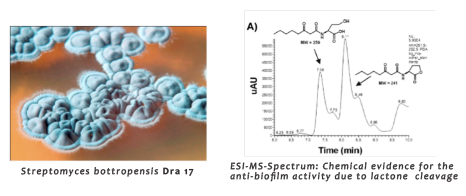 |
As the chemistry partner in the research network we aim to establish:
|
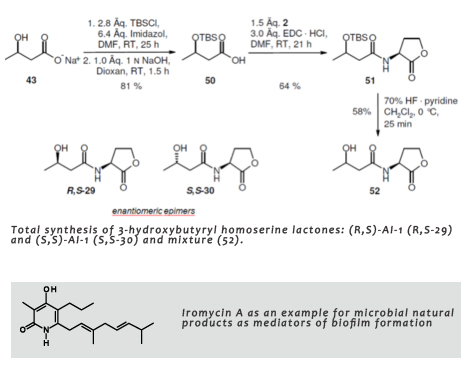 |
References: |
| C. Schipper, C. Hornung, P. Bijtenhoorn, M. Quitschau, S. Grond, W. R. Streit (2009). Metagenome-derived clones encoding for two novel lactonase family proteins involved in biofilm inhibition in P. aeruginosa. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 75, 224-233. |
| M. Quitschau (2009). Neue Biofilminhibitoren mittels Metagenom-Strategie und marine Streptomyceten, neue Naturstoffe, Synthesen und Biosynthesen. Dissertation, Georg August Universität Göttingen, Institut für organische Chemie. |
| F. Surup, H. Shojaei, P. von Zezschwitz, B. Kunze, S. Grond (2008). New Iromycins from Streptomyces sp. and Synthesis as Mitochondrial Complex I Inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem., 16, 1738-1746. |
| F. Surup, O. Wagner, J. von Frieling, M. Schleicher, S. Oess, P. Müller, S. Grond (2007). The Iromycins, a New Family of Pyridone Metabolites from Streptomyces sp.: Structure, NOS, Inhibitory Activity and Biosynthesis. J. Org. Chem., 72, 5085-5090. |
Funded by


New Brochure: Facetten der Genomforschung
Wissenschaftler entschlüsseln die Baupläne des Lebens (german; pdf; 12,3 Mb)
Wissenschaftler entschlüsseln die Baupläne des Lebens (german; pdf; 12,3 Mb)

